Superregnum: Eukaryota
Regnum: Plantae
Divisio: Tracheophyta
Divisio: Pteridophyta
Classis: Polypodiopsida
Ordo: Polypodiales
Familia: Blechnaceae
Subfamilia: Blechnoideae
Genus: Struthiopteris
Species: Struthiopteris spicant
Varietates: S. s. var. homophyllum – S. s. var. pradae – S. s. var. spicant
Source(s) of checklist:
Hassler, M. 2020. World Ferns. Checklist of Ferns and Lycophytes of the World. (Version 8.30 – April 2020). Struthiopteris spicant Accessed: 10 Apr 2020.
Name
Struthiopteris spicant (L.) Weiss, Pl. Crypt. Fl. Gött. 287 (1770).
Synonyms
Basionym
Osmunda spicant L., Sp. Pl. 2: 1066 (1753).
Homotypic
Acrostichum spicant (L.) Willd., Fl. Berol. Prodr.: 289 (1787).
Asplenium spicant (L.) Ehrh., Beitr. Naturk. 2: 95 (1788).
Asplenium spicant (L.) Bernh., J. Bot. (Schrader) 1799 [1]. 309 (1799), comb. superfl.
Blechnum spicant (L.) Roth, Ann. Bot. (Usteri) 10(4): 56 (1794).
Blechnum spicant (L.) Sm., Mém. Acad. Turin 5: 411 (1793), nom. inval..
Blechnum spicant (L.) With., Bot. Arrang. ed. 3, 3: 765 (1796), comb. superfl.
Lomaria spicant (L.) Desv., Ges. Naturf. Freunde Berlin Mag. Neuesten Entdeck. Gesammten Naturk. 5: 325 (1811).
Lonchitis-aspera spicant (L.) Farw., Amer. Midl. Naturalist 12: 277 (1931).
Onoclea spicant (L.) Hoffm., Deutschl. Fl. 2: 11 (1795).
Distribution
Native distribution areas:
Continental: Europe
Regional: Northern Europe
Denmark, Finland, Føroyar, Great Britain, Iceland, Ireland, Norway, Sweden.
Regional: Middle Europe
Austria, Belgium, Czechoslovakia (Czech Republic, Slovakia), Germany, Hungary, Netherlands, Poland, Switzerland.
Regional: Southwestern Europe
Corse, France, Portugal, Sardegna, Spain.
Regional: Southeastern Europe
Albania, Bulgaria, Greece, Italy, Kriti, Romania, Sicilia (Sicily, Malta), Turkey-in-Europe, Yugoslavia (Bosnia-Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia & Kosovo, Slovenia)
Regional: Eastern Europe
Baltic States (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania), Krym, Ukraine.
Continental: Africa
Regional: Northern Africa
Algeria, Morocco, Tunisia.
Regional: Macaronesia
Azores (Corvo, Faial, Flores, Graciosa, Pico, Santa Maria, Sao Jorge, Sao Miguel, Terceira), Canary Islands (Gomera, Tenerife), Madeira (Madeira).
Continental: Asia-Temperate
Regional: Caucasus
North Caucasus, Transcaucasus (Azerbaijan, Gruziya)
Regional: Western Asia
Iran, Lebanon-Syria (Lebanon), Turkey.
Continental: Northern America
Regional: Subarctic America
Alaska.
Regional: Western Canada
British Columbia.
Regional: Northwestern U.S.A.
Idaho, Oregon, Washington.
Regional: Southwestern U.S.A.
California.
References: Brummitt, R.K. 2001. TDWG – World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions, 2nd Edition
References
Weiss, F.W.G. 1770: Plantae Cryptogamicae Florae Gottingensis 287.
Additional references
Wasowicz, P., Gabriel y Galán, J.M. & Pino Pérez, R. 2017. New combinations in Struthiopteris spicant for the European flora. Phytotaxa 302(2): 198–200. DOI: 10.11646/phytotaxa.302.2.11 Paywall Reference page.
Molino, S., Gabriel y Galán, J.M., Sessa, E.B. & Wasowicz, P. 2019. A multi‐character analysis of Struthiopteris leads to the rescue of Spicantopsis (Blechnaceae, Polypodiopsida). Taxon 68(2): 185–198. DOI: 10.1002/tax.12036 Paywall PDF Reference page.
Molino, S., Gabriel y Galán, J.M., Wasowicz, P., de la Fuente, P. & Sessa, E.B. 2019. The Struthiopteris spicant (Blechnaceae, Polypodiopsida) complex in Western Europe, with proposals for taxonomic and nomenclatural changes. Plant Systematics and Evolution 305(4): 255–268. DOI: 10.1007/s00606-019-1565-0 Paywall Reference page.
Links
Hassler, M. 2020. World Ferns. Checklist of Ferns and Lycophytes of the World. (Version 8.30 – April 2020). Struthiopteris spicant Accessed: 10 Apr 2020.
Govaerts, R. et al. 2020. Struthiopteris spicant in Kew Science Plants of the World online. The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Published online. Accessed: 2020 Apr 10. Reference page.
International Plant Names Index. 2019. Struthiopteris spicant. Published online. Accessed: May 06 2019.
Tropicos.org 2019. Struthiopteris spicant. Missouri Botanical Garden. Published online. Accessed: 06 May 2019.
USDA, ARS, Germplasm Resources Information Network. Struthiopteris spicant in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), U.S. Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service. Accessed: 08-Apr-12.
Vernacular names
مصرى: بلخنون سنبلى
العربية: بلخنون سنبلي
čeština: Žebrovice různolistá
Cymraeg: Gwibredynen gwibredyn
dansk: Kambregne
Deutsch: Rippenfarn
English: Hard Fern
español: Doradilla de bosque
eesti: Tähk-roodjalg
euskara: Orrazi-iratze
فارسی: سرخس آهو
suomi: Kaitakampasulka
français: Blechnum en épi
galego: Fento fero
magyar: Erdei bordapáfrány
íslenska: Skollakambur
Nederlands: Dubbelloof
norsk: Bjønnkam
polski: Podrzeń żebrowiec
русский: Дербянка колосистая
slovenčina: Rebrovka rôznolistá
српски / srpski: Rebrača
svenska: Kambräken
українська: Ребрівка звичайна
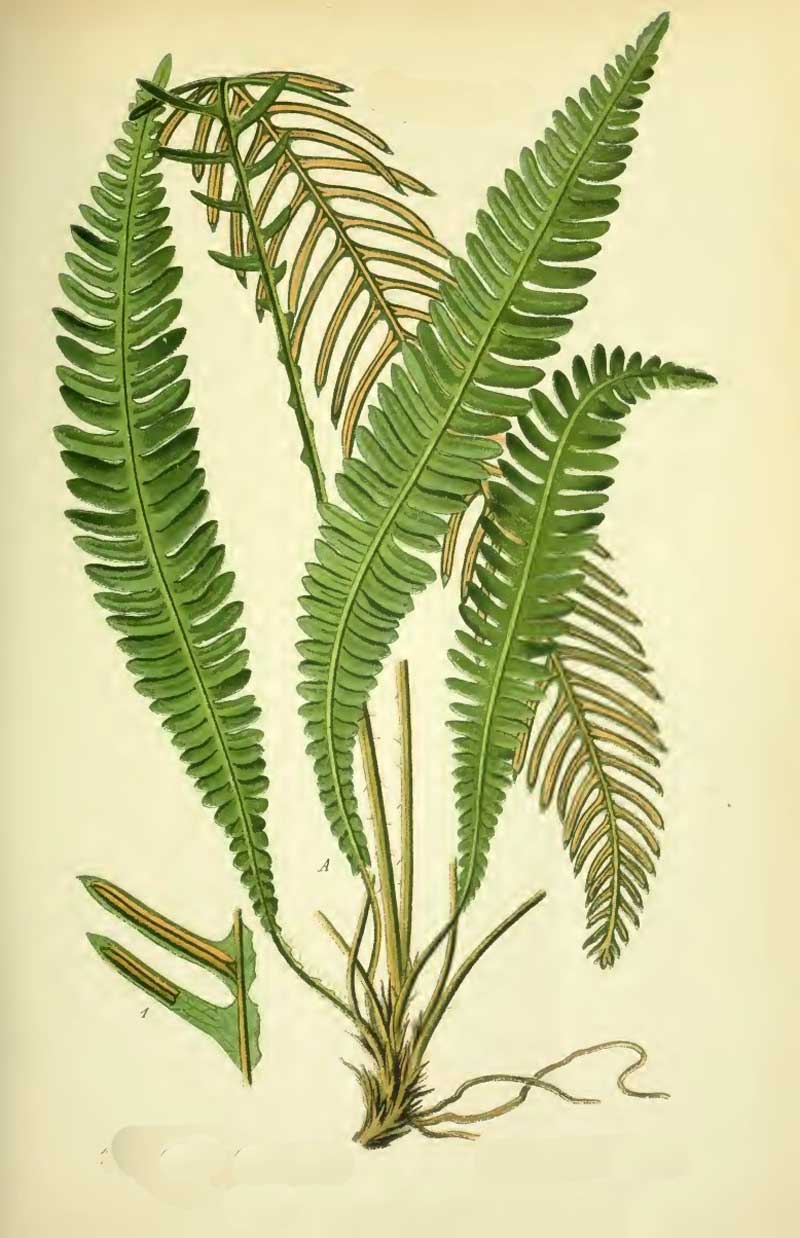
Struthiopteris spicant, syn. Blechnum spicant, is a species of fern in the family Blechnaceae, known by the common names hard-fern[3] or deer fern. It is native to Europe, western Asia, northern Africa, and western North America.[1][4] Like some other species in the family Blechnaceae, it has two types of leaves. The sterile leaves have flat, wavy-margined leaflets 5 to 8 millimeters wide, while the fertile leaves have much narrower leaflets, each with two thick rows of sori on the underside.[5]
The Latin specific epithet spicant is of uncertain origin, possibly referring to a tufted or spiky habit.[6]
S. spicant is hardy down to −20 °C (−4 °F) and evergreen, growing to 0.5 m (1 ft 8 in).[7] It has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit.[8]
The species was first described in 1753 by Carl Linnaeus as Osmunda spicant. It has been placed in a wide range of genera, including Blechnum (as Blechnum spicant).[1] In the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I), it is placed in the genus Struthiopteris, in the subfamily Blechnoideae.[9]
References
"Blechnum spicant (L.) Roth". Plants of the World Online. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 2019-08-12.
Gasper, André Luís De; Dittrich, Vinícius Antonio De Oliveira; Smith, Alan Reid & Salino, Alexandre (2016-09-21). "A classification for Blechnaceae (Polypodiales: Polypodiopsida): New genera, resurrected names, and combinations". Phytotaxa. 275 (3): 191–227. doi:10.11646/phytotaxa.275.3.1. ISSN 1179-3163. Retrieved 2019-08-11.
BSBI List 2007 (xls). Botanical Society of Britain and Ireland. Archived from the original (xls) on 2015-06-26. Retrieved 2014-10-17.
USDA Plants Profile
Jepson Manual Treatment
Harrison, Lorraine (2012). RHS Latin for Gardeners. United Kingdom: Mitchell Beazley. ISBN 978-1845337315.
RHS A-Z encyclopedia of garden plants. United Kingdom: Dorling Kindersley. 2008. p. 1136. ISBN 978-1405332965.
"RHS Plant Selector - Blechnum spicant". Retrieved 15 April 2020.
PPG I (2016). "A community-derived classification for extant lycophytes and ferns". Journal of Systematics and Evolution. 54 (6): 563–603. doi:10.1111/jse.12229. S2CID 39980610.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License

