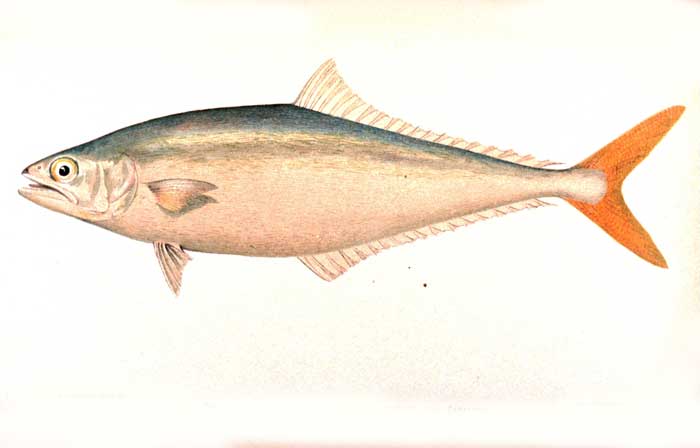
Oligoplites saurus
Superregnum: Eukaryota
Cladus: Unikonta
Cladus: Opisthokonta
Cladus: Holozoa
Regnum: Animalia
Subregnum: Eumetazoa
Cladus: Bilateria
Cladus: Nephrozoa
Superphylum: Deuterostomia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Infraphylum: Gnathostomata
Megaclassis: Osteichthyes
Superclassis/Classis: Actinopterygii
Classis/Subclassis: Actinopteri
Subclassis/Infraclassis: Neopterygii
Infraclassis: Teleostei
Megacohors: Osteoglossocephalai
Supercohors: Clupeocephala
Cohors: Euteleosteomorpha
Subcohors: Neoteleostei
Infracohors: Eurypterygia
Sectio: Ctenosquamata
Subsectio: Acanthomorphata
Divisio/Superordo: Acanthopterygii
Subdivisio: Percomorphaceae
Series: Eupercaria
Ordo: Perciformes
Subordo: Percoidei
Superfamilia: Percoidea
Familia: Carangidae
Genus: Oligoplites
Species: O. saurus
The leatherjacket fish (Oligoplites saurus), also known as leather jack, is a species of jack in the family Carangidae.[4] Leather jack may also refer to other members of the Carangidae, such as the pilot fish. The largest are about a foot long.[5]
Distribution
There are two subspecies of Oligoplites saurus. The nominate subspecies O.s. saurus is distributed in the western Atlantic Ocean from Chatham, Massachusetts south along the U.S. coast, throughout the Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea, and along the South American coast to Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. The other subspecies O. s. inornatus is found in the eastern Pacific Ocean from southern Baja California, much of the Gulf of California to Ecuador, including the Galapagos and Malpelo Islands.[1]
Feeding
It voraciously devours small fish and shrimp, often in company with larger predatory species. Leatherjackets feed on small fish including the silver perch.
As food
Traditionally, the leather jacket has not been eaten, but recently, with large-scale farming of the fish, it has become common at market[where?]. The fish has a mild, oily taste similar to Spanish mackerel or bluefish.
It has occasionally been the prey to blue swimmer crab, as juvenile fish in sea grass beds.
References
Smith-Vaniz, W.F.; Williams, J.T.; Pina Amargos, F.; Curtis, M.; Brown, J.; Vega-Cendejas, M. (2019). "Oligoplites saurus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T183364A86338645. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T183364A86338645.en. Retrieved 20 November 2021.
Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2019). "Oligoplites saurus" in FishBase. August 2019 version.
Eschmeyer, William N.; Fricke, Ron & van der Laan, Richard (eds.). "Species in the genus Oligoplites". Catalog of Fishes. California Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 19 November 2019.
"Oligoplites saurus". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 24 January 2006.
"Home". Gulf Of Maine Research Institute. Retrieved 2021-05-23.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License

