Crocodylus porosus (*) Cladus: Eukaryota
Crocodylus porosus (*) Name Crocodylus porosus Schneider, 1801 Type locality: Unknown; designated as "Ceylon" (=Sri Lanka) by Mertens (1960: 271) Holotype: Lectotype ZMB 278 (Crocodilus porosus Schneider, 1801; see Mertens, 1960), holotype BMNH [Oopholis pondicherianus Gray, 1862] Synonyms * Crocodylus natans Meyer, 1795 (nomen oblitum)
* Schneider, Johann Gottlob 1801. "Historiae Amphibiorum naturalis et literariae. Fasciculus secundus continens Crocodilos, Scincos, Chamaesauras, Boas. Pseudoboas, Elapes, Angues. Amphisbaenas et Caecilias." Frommani, Jena. 374 pp.
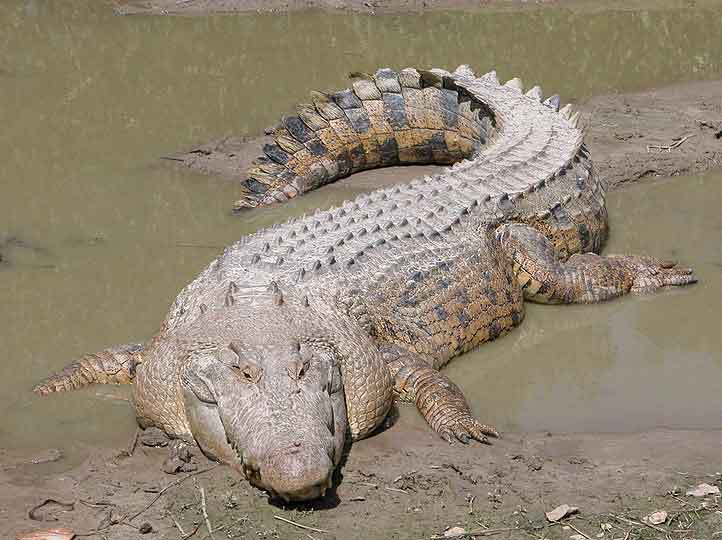
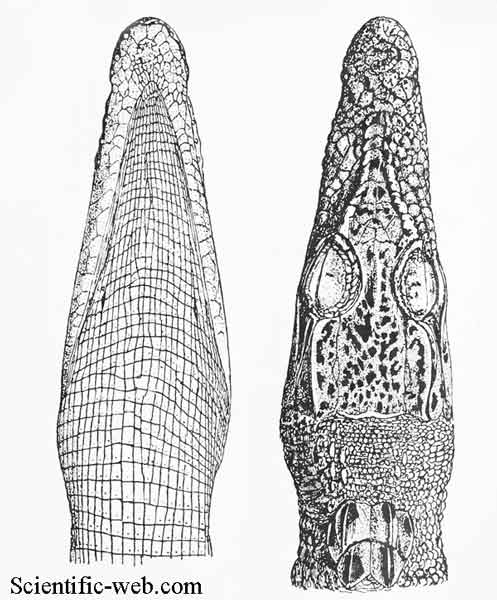
The saltwater or estuarine crocodile (Crocodylus porosus) is the largest of all living reptiles. It is found in suitable habitats in Northern Australia, the eastern coast of India and parts of Southeast Asia. Anatomy and morphology The saltwater crocodile has a longer muzzle than the mugger crocodile: its length is twice its breadth at the base.[1] The saltwater crocodile has fewer armor plates on its neck than other crocodilians, and its broad body contrasts with that of most other lean crocodiles, leading to early unverified assumptions that the reptile was an alligator.[2] An adult male saltwater crocodile's weight is 600 to 1,000 kilograms (1,300–2,200 lb) and length is normally 4.1 to 5.5 metres (13–18 ft), although mature males can be 6 metres (20 ft) or more and weigh 1,300 kilograms (2,900 lb) or larger.[3][4][5] This species has the greatest sexual dimorphism of any modern crocodilian, with females being much smaller than males. Typical female body lengths in the range of 2.1 to 3.5 metres (7–11 ft).[2][6][7] The largest female on record measured about 4.2 metres (14 ft).[5] The mean weight of the species as a whole is roughly 450 kilograms (1,000 lb).[8] The largest size saltwater crocodiles can reach is the subject of considerable controversy. The longest crocodile ever measured snout-to-tail and verified was the skin of a dead crocodile, which was 6.1 metres (20 ft) long. As skins tend to shrink slightly after removal from the carcass, this crocodile's living length was estimated at 6.3 metres (21 ft), and it probably weighed well over 1,200 kilograms (2,600 lb).[9] Incomplete remains (the skull of a crocodile shot in Orissa[10]) have been claimed to come from a 7.6-metre (25 ft) crocodile, but scholarly examination suggested a length no greater than 7 metres (23 ft).[9] There have been numerous claims of crocodiles in the 9-metre (30 ft) range: the crocodile shot in the Bay of Bengal in 1840, reported at 10 metres (33 ft); another killed in 1823 at Jalajala on the main island of Luzon in the Philippines reported at 8.2 metres (27 ft); a reported 7.6 metres (25 ft) crocodile killed in the Hooghly River in the Alipore District of Calcutta. However, examinations of these animals' skulls actually indicated animals ranging from 6 to 6.6 metres (20–21.7 ft). With recent restoration of saltwater crocodile habitat and reduced poaching, it is possible that 7-metre (23 ft) crocodiles are alive today.[11] Guinness has accepted a claim of a 7-metre (23 ft) male saltwater crocodile living within Bhitarkanika Park in the state of Orissa, India,[10][12] although, due to the difficulty of trapping and measuring a very large live crocodile, the accuracy of these dimensions has yet to be verified. A crocodile shot in Queensland in 1957 was reported to be 8.5 metres (28 ft) long, but no verified measurements were made and no remains of this crocodile exist. A "replica" of this crocodile has been made as a tourist attraction.[13][14][15] Many other unconfirmed reports of 8+ metres (28+ ft) crocodiles have been made[16][17] but these are highly unlikely. Distribution
In northern Australia (which includes the northernmost parts of the Northern Territory, Western Australia and Queensland) the Saltwater Crocodile is thriving, particularly in the multiple river systems near Darwin (such as the Adelaide, Mary and Daly Rivers, along with their adjacent billabongs and estuaries) where large (6 metre +) individuals are common. The Australian Saltwater Crocodile population is estimated at somewhere between 100,000 and 200,000 adults. Their range extends from Broome in Western Australia through the entire Northern Territory coast all the way down to Rockhampton in Queensland. The Alligator Rivers of Northern Australia are misnamed due to the resemblance of the saltwater crocodile to alligators as compared to freshwater crocodiles, which also inhabit the Northern Territory. In New Guinea they are also common, existing within the coastal reaches of virtually every river system in the country, along with all estuaries and mangroves. They are also present in varying numbers throughout the Bismarck Archipelago, the Kai Islands, the Aru Islands, the Maluku Islands, and many other islands within the region including Timor, and most islands within the Torres Strait. The saltwater crocodile was historically found throughout Southeast Asia but is now extinct throughout much of this range. This species has not been reported in the wild for decades in most of Indochina and is extinct in Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, and possibly Cambodia. The status of this species is critical within much of Myanmar, but there is a stable population of many large adults present in the Irrawaddy Delta.[19] It is probable that the only country in Indochina still harboring wild populations of this species is Myanmar. Although Saltwater Crocodiles were once very common in the Mekong Delta (from where they disappeared in the 1980s) and other river systems, the future of this species in Indochina is now looking grim. However, it is also the least likely of crocodilians to become globally extinct due to its wide distribution and almost pre-colonial population sizes in Northern Australia and New Guinea. The population is sporadic in Indonesia and Malaysia with some areas harboring large populations (Borneo, for example) and others with very small, at-risk populations (e.g., the Philippines). The status of this species is largely unknown within Sumatra and Java (although recent reports of attacks on humans by large crocodiles within isolated regions of Sumatra have been reported by news agencies and deemed reliable.) Despite the close proximity to the crocodile hot-bed of northern Australia, crocodiles no longer exist in Bali. The saltwater crocodile is also present in very limited parts of the South Pacific, with an average population in the Solomon Islands, a very small, invasive and soon to be extinct population in Vanuatu (where the population officially stands at only three) and a decent but at-risk population (which may be rebounding) in Palau. Saltwater crocodiles once ranged as far west as the east coast of Africa at the Seychelles Islands. These crocodiles were once believed to be a population of Nile crocodiles, but they were later proven to be Crocodylus porosus.[2] Due to this species' tendency to travel very long distances at sea, individual saltwater crocodiles occasionally show up in odd locales where they are not native. Vagrant individuals have historically been reported on New Caledonia, Iwo Jima, Fiji, and even in the relatively frigid Sea of Japan (thousands of miles from their native territory.) In late 2008/early 2009 a handful of wild saltwater crocodiles were verified to be living within the river systems of Fraser Island, hundreds of kilometers from and in much cooler water than their normal Queensland range. It was discovered that these crocodiles did indeed migrate south to the island from northern Queensland during the warmer wet season and presumably returned to the north upon the seasonal temperature drop. Despite the surprise and shock within the Fraser Island public, this is apparently not new behavior and in the distant past wild crocodiles had been reported occasionally appearing as far south as Brisbane during the warmer wet season. Habitat Saltwater crocodiles generally spend the tropical wet season in freshwater swamps and rivers, moving downstream to estuaries in the dry season, and sometimes traveling far out to sea. Crocodiles compete fiercely with each other for territory, with dominant males in particular occupying the most eligible stretches of freshwater creeks and streams. Junior crocodiles are thus forced into the more marginal river systems and sometimes into the ocean. This explains the large distribution of the animal (ranging from the east coast of India to northern Australia) as well as its being found in odd places on occasion (such as the Sea of Japan). Saltwater crocodiles can swim 15 to 18 miles per hour (6.7 to 8.0 m/s) in short bursts, but when cruising go 2 to 3 mph (0.9 to 1.3 m/s). Diet and behaviour
It usually waits for its prey to get close to the water's edge before striking, using its great strength to drag the animal back into the water. Most prey animals are killed by the great jaw pressure of the crocodile, although some animals may be incidentally drowned. It is a powerful animal, having the strength to drag a fully grown water buffalo into a river, or crush a full-grown bovid's skull between its jaws. Its typical hunting technique is known as the "death roll": it grabs onto the animal and rolls powerfully. This throws any struggling large animal off balance, making it easier to drag it into the water. The "death roll" is also used for tearing apart large animals once they are dead. Baby saltwater crocodiles may fall prey to monitor lizards, predatory fish, birds, and many other predators. Juveniles may also fall prey to Bengal tigers and leopards in certain parts of their range, although this is rare.. Intelligence One researcher, Dr. Adam Britton,[23] has been studying crocodilian intelligence. He has compiled a collection of Australian saltwater crocodile calls,[24] and associated them with behaviors. His position is that while crocodilian brains are much smaller than those of mammals (as low as 0.05% of body weight in the saltwater crocodile), they are capable of learning difficult tasks with very little conditioning. He also infers that the crocodile calls hint at a deeper language ability than currently accepted. He suggests that saltwater crocodiles are clever animals that can possibly learn faster than lab rats. They have also learned to track the migratory route of their prey as the seasons change. Attacks on humans Data on attacks is limited outside of Australia. In Australia, attacks are rare and usually appear in national news publications when they do occur. There are approximately one to two fatal attacks reported per year in the country.[25] The low level of attacks may be due to extensive efforts by wildlife officials in Australia to post crocodile warning signs at many at-risk billabongs, rivers, lakes and beaches. In the large Aboriginal community of Arnhem Land, attacks may go unreported. There have also been recent, less-publicised attacks in Borneo,[26] Sumatra,[27] eastern India (Andaman Islands),[28][29] and in Myanmar.[30] During the Japanese retreat in the Battle of Ramree Island on February 19, 1945, saltwater crocodiles may have been responsible for the deaths of 400 Japanese soldiers. British soldiers encircled the swampland through which the Japanese were retreating, resigning the Japanese to a night in the mangroves which was home to thousands of saltwater crocodiles. The Ramree crocodile attacks are listed under the heading "The Greatest Disaster Suffered from Animals" in The Guinness Book of Records [31] Notes 1. ^ Guggisberg, C.A.W. (1972). Crocodiles: Their Natural History, Folklore, and Conservation. p. 195. ISBN 0715352725.
* Crocodile Specialist Group (1996). Crocodylus porosus. 2006. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. IUCN 2006. www.iucnredlist.org. Retrieved on 9 May 2006. Source: Wikipedia, Wikispecies: All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License |
|