.
Aquila (constellation)
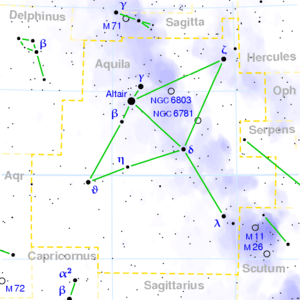
Aquila ( Latin: eagle; sometimes named the Vulture), is one of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy, also mentioned by Eudoxus (4th century BC) and Aratus (3rd century BC) and now also part of the list of 88 constellations acknowledged by the IAU. It lies roughly at the celestial equator. The alpha star, Altair, is a vertex of the Summer Triangle asterism.
 |
|
| List of stars in Aquila | |
| Abbreviation: | Aql |
| Genitive: | Aquilae |
| Symbology: | the Eagle |
| Right ascension: | 20 h |
| Declination: | +5° |
| Area: | 652 sq. deg. (22nd) |
| Main stars: | 8 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars: | 61 |
| Stars known to have planets: | 3 |
| Bright stars: | |
| Nearby stars: | 3 |
| Brightest star: | Altair (α Aql) (0.77m) |
| Nearest star: | Altair (α Aql) (16.72 ly) |
| Messier objects: | 0 |
| Meteor showers: | June Aquilids Epsilon Aquilids |
| Bordering constellations: | Sagitta Hercules Ophiuchus Serpens Cauda Scutum Sagittarius Capricornus Aquarius Delphinus |
| Visible at latitudes between +85° and −75° Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of August |
|
Ptolemy catalogued nineteen stars jointly in this constellation and in the constellation Antinous, which was named in the reign of the emperor Hadrian (AD 117–138), but sometimes, and wrongly, attributed to Tycho Brahe, who catalogued twelve stars in Aquila and seven in Antinous; Hevelius determined twenty-three stars in the first, and nineteen in the second. NASA's Pioneer 11 mission, which flew by Jupiter and Saturn (in 1974 and 1979 respectively) will pass near one of the stars in the constellation in about four million years.
Notable features
Aquila, which lies in the Milky Way, contains many rich starfields.
* α Aql (Altair): this multiple star system (3 components) has 0.77m and is of spectral type A7 V. It has a parallax of 0.23", and consequently is about eight times as bright as the sun.
* β Aql (Alshain): its spectral type is G8 IV and it shines with an apparent brightness of 3.71m. Like Altair, it too is a multiple star system with three components.
* γ Aql (Tarazed): spectral type K3 II; 2.72m
* η Aql: This short-period variable star is one of the brightest classical Cepheids; its brightness varies between 3.48 mag and 4.39 mag every 7.177 days.
* 15 Aql: This double star is a yellow K star of 5.4 mag accompanied by a 7th mag star; it can easily be observed with small telescopes.
Notable deep-sky objects
Three interesting planetary nebulae lie in Aquila:
* NGC 6804 shows a small but bright ring
* NGC 6781 which bears some resemblance with the Owl Nebula in Ursa Major.
* NGC 6751: also known as the Glowing Eye, a planetary nebula
More deep-sky objects:
* NGC 6709: an open cluster of 6.7m located five degrees southwest of Zeta Aquilae
* NGC 6755: an open cluster of 7.5m; it is made up of about a dozen stars with magnitudes 12 thru 13
* NGC 6760: a globular cluster of 9.1m
* NGC 6749: an open cluster
* NGC 6778: planetary nebula
* NGC 6741: planetary nebula
* NGC 6772: planetary nebula
This Constellation is most best seen in September(9:00p.m)
History
The major novae have been observed in Aquila; the first one was in 389 BC and was recorded to be as bright as Venus, the other (Nova Aquilae 1918) briefly shone brighter than Altair, the brightest star in Aquila. Depicted as an eagle, Aquila is named for the bird that belonged to Zeus. Aquila's most famous task was carrying the mortal Ganymede to the heavens to serve as Zeus' cup bearer.
Mythology
The constellation resembles a wide winged, soaring, short necked, bird, which the ancients identified as an eagle [1]. In classical Greek mythology, it was identified as the eagle which carried the thunderbolts of Zeus and was sent by him to carry the shepherd boy Ganymede who he desired, represented by the neighbouring Aquarius, to Mount Olympus where he became the wine-pourer for all the gods. This explains why the largest moon of Jupiter was called Ganymede, Jupiter being the Roman name of Zeus. The eagle was used to carry or retrieve the lightning bolts that were thrown by Zeus.
This constellation was also known as Vultur volans to the Romans, not to be confused with Vultur cadens which was the Romans' name for what is now known as Lyra.
Aquila, together with other constellations in the Zodiac sign of Sagittarius (specifically, Lyra, Cygnus), may be a significant part of the origin of the myth of the Stymphalian birds, one of The Twelve Labours of Herakles. The constellation could also have originated from the eagle Ethon, the tormentor of Prometheus, and offspring of the monsters Typhon and Echidna.
In the Chinese love story of Qi Xi, Niu Lang (Altair) and his two children (β and γ Aquilae) are separated forever from their wife and mother Zhi Nu (Vega) who is on the far side of the river, the Milky Way.
In Hinduism, the Aquila consellation is identified with the half eagle, half human deity, Garuda.

Delphinus, Sagitta, Aquila, and Antinous
References
* This article incorporates text from the Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition, a publication now in the public domain.
* Ian Ridpath and Wil Tirion (2007). Stars and Planets Guide, Collins, London. ISBN 978-0007251209. Princeton University Press, Princeton. ISBN 978-0691135564.
Links
|
The 88 modern constellations
Andromeda | Antlia | Apus | Aquarius | Aquila | Ara | Aries | Auriga | Boötes | Caelum | Camelopardalis | Cancer | Canes Venatici | Canis Major | Canis Minor | Capricornus | Carina | Cassiopeia | Centaurus | Cepheus | Cetus | Chamaeleon | Circinus | Columba | Coma Berenices | Corona Australis | Corona Borealis | Corvus | Crater | Crux | Cygnus | Delphinus | Dorado | Draco | Equuleus | Eridanus | Fornax | Gemini | Grus | Hercules | Horologium | Hydra | Hydrus | Indus | Lacerta | Leo | Leo Minor | Lepus | Libra | Lupus | Lynx | Lyra | Mensa | Microscopium | Monoceros | Musca | Norma | Octans | Ophiuchus | Orion | Pavo | Pegasus | Perseus | Phoenix | Pictor | Pisces | Piscis Austrinus | Puppis | Pyxis | Reticulum | Sagitta | Sagittarius | Scorpius | Sculptor | Scutum | Serpens | Sextans | Taurus | Telescopium | Triangulum | Triangulum Australe | Tucana | Ursa Major | Ursa Minor | Vela | Virgo | Volans | Vulpecula |
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License

