.
Ara (constellation)
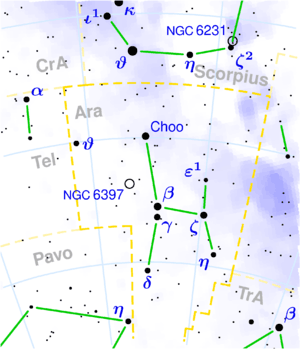
Ara ( Latin: altar) is a southern constellation situated between the constellations Scorpius and Triangulum Australe.
Notable features
Ara's brightest star, β Arae, has an apparent magnitude of 2.9. γ Arae is a double star just south of β. μ Arae is believed to have at least four planets orbiting it, one of which may be rocky in nature. ά Arae has the name Choo, Chinese for club or staff. Epsilon Arae, έ Arae, has the name Tso Kang, meaning left guard.
Notable deep sky objects
The northwest corner of Ara is crossed by the Milky Way and contains several open clusters and diffuse nebulae. The brightest of the globular clusters, NGC 6397, is 8,200 light-years from our solar system and may be the closest cluster of that kind.
History
This constellation was one of Ptolemy's original 48 constellations.
Mythology
In ancient greek mythology, it was thought that the Cyclopes orginally built the altar as a place to sacrifice to the Olympian gods. The altar, usually depicted upside down, but sometimes upright with the smoke drifting into the Milky Way, was identified as the altar of Lycaon. Lycaon sacrificed a child (according to one legend, it was Arcas) to Zeus on the altar on mount Lycaeus, and immediately after the sacrifice was turned into a wolf, which may have also formed the basis for the myth of the constellation Lupus.
In other greek tales, Ara was identified with the altar of the god of wine, Dionysus.
Ara was also sometimes identified with that of the centaur Chiron; its original Latin name was Ara Centauri.
References
* Ian Ridpath and Wil Tirion (2007). Stars and Planets Guide, Collins, London. ISBN 978-0007251209. Princeton University Press, Princeton. ISBN 978-0691135564.
Links
|
The 88 modern constellations
Andromeda | Antlia | Apus | Aquarius | Aquila | Ara | Aries | Auriga | Boötes | Caelum | Camelopardalis | Cancer | Canes Venatici | Canis Major | Canis Minor | Capricornus | Carina | Cassiopeia | Centaurus | Cepheus | Cetus | Chamaeleon | Circinus | Columba | Coma Berenices | Corona Australis | Corona Borealis | Corvus | Crater | Crux | Cygnus | Delphinus | Dorado | Draco | Equuleus | Eridanus | Fornax | Gemini | Grus | Hercules | Horologium | Hydra | Hydrus | Indus | Lacerta | Leo | Leo Minor | Lepus | Libra | Lupus | Lynx | Lyra | Mensa | Microscopium | Monoceros | Musca | Norma | Octans | Ophiuchus | Orion | Pavo | Pegasus | Perseus | Phoenix | Pictor | Pisces | Piscis Austrinus | Puppis | Pyxis | Reticulum | Sagitta | Sagittarius | Scorpius | Sculptor | Scutum | Serpens | Sextans | Taurus | Telescopium | Triangulum | Triangulum Australe | Tucana | Ursa Major | Ursa Minor | Vela | Virgo | Volans | Vulpecula |
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License