|
|
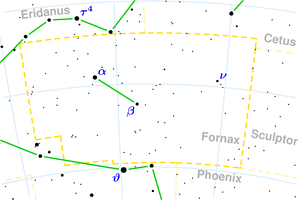
Fornax ( Latin: furnace) is a southern constellation which was first introduced by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille under the name Fornax Chemica (Latin for chemical furnace), representing a small solid-fuel heater formerly used for heating chemical experiments. The Fornax Dwarf galaxy is in Fornax. The Hubble Ultra Deep Field is located within Fornax. At a meeting of the Royal Astronomical Society in Britain, a team from University of Queensland described 40 unknown "dwarf" galaxies in this constellation. They also described Fornax as being "on Earth's doorstep", because α Fornacis is only about 46 light-years away. Follow-up observations with the Hubble Space Telescope and the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope revealed that Ultra Compact Dwarfs are much smaller than previously known dwarf galaxies, about 120 light-years across. "Tens of millions of stars are squashed into what is a tiny volume by galaxy standards," the observatory said in a statement. The Fornax Cluster, a small cluster of galaxies lies primarily in the constellation Fornax. Mythology In Roman mythology, Fornax was the goddess of bread and baking, although this has nothing to do with the constellation (fornax is just the Roman word for furnace), as the constellation was created in 1756. Deep sky objects NGC 1316 is a notably bright elliptical galaxy within the Fornax Cluster. The galaxy is also one of the brightest radio sources in the sky. References * Ian Ridpath and Wil Tirion (2007). Stars and Planets Guide Links
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||